Spring Boot @ConfigurationProperties example
Spring Boot @ConfigurationProperties is letting developer maps the entire .properties and yml file into an object easily.
P.S Tested with Spring Boot 2.1.2.RELEASE
1. @Value
1.1 Normally, we use the @Value to inject the .properties value one by one, this is good for small and simple structure .properties files. For example,
email=test@mkyong.com thread-pool=12
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:global.properties")
public class GlobalProperties {
@Value("${thread-pool}")
private int threadPool;
@Value("${email}")
private String email;
//getters and setters
1.2 The equivalent in @ConfigurationProperties
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:global.properties")
@ConfigurationProperties
public class GlobalProperties {
private int threadPool;
private String email;
//getters and setters
2. @ConfigurationProperties
2.1 Review a complex structure .properties or yml file below, how we are going to map the values via @Value?
#Logging logging.level.org.springframework.web=ERROR logging.level.com.mkyong=DEBUG #Global email=test@mkyong.com thread-pool=10 #App app.menus[0].title=Home app.menus[0].name=Home app.menus[0].path=/ app.menus[1].title=Login app.menus[1].name=Login app.menus[1].path=/login app.compiler.timeout=5 app.compiler.output-folder=/temp/ app.error=/error/
or the equivalent in YAML.
logging:
level:
org.springframework.web: ERROR
com.mkyong: DEBUG
email: test@mkyong.com
thread-pool: 10
app:
menus:
- title: Home
name: Home
path: /
- title: Login
name: Login
path: /login
compiler:
timeout: 5
output-folder: /temp/
error: /error/
@ConfigurationProperties supports both .properties and .yml file.
2.2 @ConfigurationProperties comes to rescue :
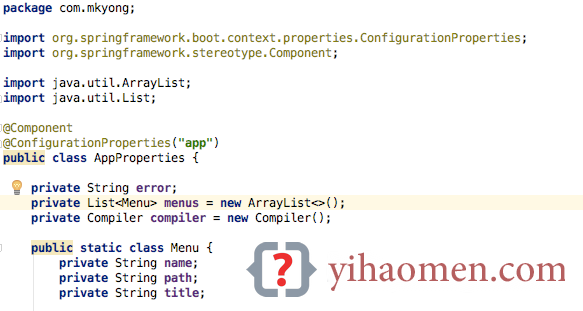
package com.mkyong;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("app") // prefix app, find app.* values
public class AppProperties {
private String error;
private List<Menu> menus = new ArrayList<>();
private Compiler compiler = new Compiler();
public static class Menu {
private String name;
private String path;
private String title;
//getters and setters
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Menu{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", path='" + path + '\'' +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
'}';
public static class Compiler {
private String timeout;
private String outputFolder;
//getters and setters
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Compiler{" +
"timeout='" + timeout + '\'' +
", outputFolder='" + outputFolder + '\'' +
'}';
//getters and setters
package com.mkyong;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties // no prefix, find root level values.
public class GlobalProperties {
private int threadPool;
private String email;
//getters and setters
3. @ConfigurationProperties Validation
This @ConfigurationProperties support JSR-303 bean validation.
3.1 Add @Validated on the @ConfigurationProperties class, and javax.validation annotations on the fields we want to validate.
package com.mkyong;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties
@Validated
public class GlobalProperties {
@Max(5)
@Min(0)
private int threadPool;
@NotEmpty
private String email;
//getters and setters
3.2 Set thread-pool=10
#Global email=test@mkyong.com thread-pool=10
3.3 Start Spring Boot and we will hits the following error message :
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************
Description:
Binding to target org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.BindException:
Failed to bind properties under '' to com.mkyong.GlobalProperties failed:
Property: .threadPool
Value: 10
Origin: class path resource [application.properties]:7:13
Reason: must be less than or equal to 5
Action:
Update your application's configuration
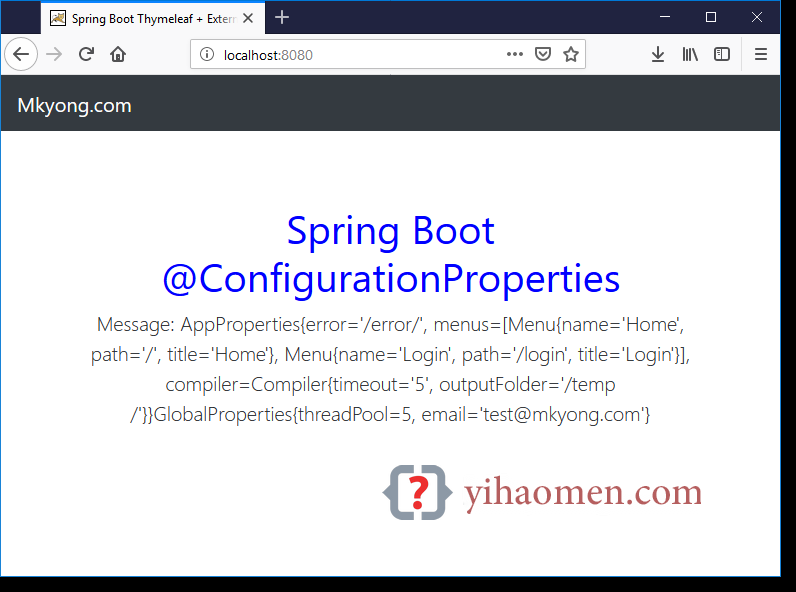
4. DEMO
$ git clone https://github.com/mkyong/spring-boot.git $ cd externalize-config-properties-yaml $ mvn spring-boot:run access localhost:8080
For more detail, please refer to this official Spring Boot Externalized Configuration
From:一号门
Previous:Java 8 Math Exact examples

COMMENTS