Spring Boot + Spring Data MongoDB example
In this article, we will show you how to create a Spring Boot + Spring Data MongoDB application, using Gradle build tool.
- Spring Boot 1.5.1.RELEASE
- MongoDB
- Gradle
- Java 8
1. Project Structure
A standard project structure.
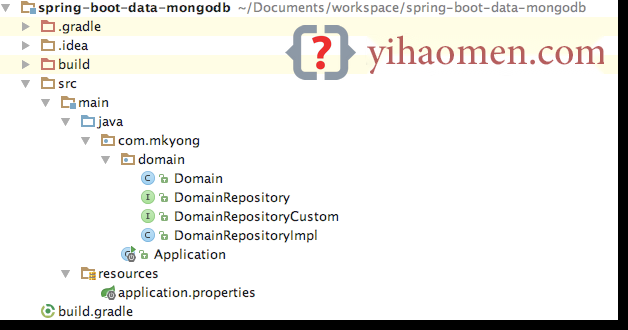
2. Project Dependency
2.1 A Gradle build file.
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:1.5.1.RELEASE")
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'idea'
apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot'
jar {
baseName = 'spring-data-mongodb-example'
version = '1.0'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
targetCompatibility = 1.8
dependencies {
compile 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb'
2.2 Declares a spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb, and it grabs a ton of libraries, review the following dependencies :
$ gradle dependencies --configuration runtime
:dependencies
------------------------------------------------------------
Root project
------------------------------------------------------------
runtime - Runtime classpath for source set 'main'.
\--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb: -> 1.5.1.RELEASE
+--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:1.5.1.RELEASE
| +--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot:1.5.1.RELEASE
| | +--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | \--- org.springframework:spring-context:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | +--- org.springframework:spring-aop:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | | +--- org.springframework:spring-beans:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | | | \--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | | \--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | +--- org.springframework:spring-beans:4.3.6.RELEASE (*)
| | +--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | \--- org.springframework:spring-expression:4.3.6.RELEASE
| | \--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
| +--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure:1.5.1.RELEASE
| | \--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot:1.5.1.RELEASE (*)
| +--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-logging:1.5.1.RELEASE
| | +--- ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:1.1.9
| | | +--- ch.qos.logback:logback-core:1.1.9
| | | \--- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.22
| | +--- org.slf4j:jcl-over-slf4j:1.7.22
| | | \--- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.22
| | +--- org.slf4j:jul-to-slf4j:1.7.22
| | | \--- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.22
| | \--- org.slf4j:log4j-over-slf4j:1.7.22
| | \--- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.22
| +--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
| \--- org.yaml:snakeyaml:1.17
+--- org.mongodb:mongodb-driver:3.4.1
| +--- org.mongodb:mongodb-driver-core:3.4.1
| | \--- org.mongodb:bson:3.4.1
| \--- org.mongodb:bson:3.4.1
\--- org.springframework.data:spring-data-mongodb:1.10.0.RELEASE
+--- org.springframework:spring-tx:4.3.6.RELEASE
| +--- org.springframework:spring-beans:4.3.6.RELEASE (*)
| \--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
+--- org.springframework:spring-context:4.3.6.RELEASE (*)
+--- org.springframework:spring-beans:4.3.6.RELEASE (*)
+--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
+--- org.springframework:spring-expression:4.3.6.RELEASE (*)
+--- org.springframework.data:spring-data-commons:1.13.0.RELEASE
| +--- org.springframework:spring-core:4.3.6.RELEASE
| +--- org.springframework:spring-beans:4.3.6.RELEASE (*)
| +--- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.22
| \--- org.slf4j:jcl-over-slf4j:1.7.22 (*)
+--- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.22
\--- org.slf4j:jcl-over-slf4j:1.7.22 (*)
3. MongoDB Configuration
#mongodb spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost spring.data.mongodb.port=27017 spring.data.mongodb.database=app1 #logging logging.level.org.springframework.data=debug logging.level.=error
4. Spring Data – MongoRepository
4.1 A simple model with Spring data annotations.
package com.mkyong.domain;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Indexed;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
@Document(collection = "domain")
public class Domain {
@Id
private long id;
@Indexed(unique = true)
private String domain;
private boolean displayAds;
//getters and setters
4.2 Extends MongoRepository, you have CRUD function automatically. Spring data come with many magic findBy queries, review the official Spring data MongoDB – Query methods for detail.
package com.mkyong.domain;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.Query;
import java.util.List;
// No need implementation, just one interface, and you have CRUD, thanks Spring Data
public interface DomainRepository extends MongoRepository<Domain, Long> {
Domain findFirstByDomain(String domain);
Domain findByDomainAndDisplayAds(String domain, boolean displayAds);
//Supports native JSON query string
@Query("{domain:'?0'}")
Domain findCustomByDomain(String domain);
@Query("{domain: { $regex: ?0 } })")
List<Domain> findCustomByRegExDomain(String domain);
4.3 To create a custom method for the DomainRepository, you need to create the implementation in another file and make the DomainRepository extends it.
The following example adds a custom ‘update a particular field’ method to MongoRepository
4.3.1 Custom Interface
package com.mkyong.domain;
public interface DomainRepositoryCustom {
int updateDomain(String domain, boolean displayAds);
4.3.2 The implementation class name is very strict, the name must be "CoreRepositoryInterface" + Impl, read this Spring data MongoDB Custom implementations
package com.mkyong.domain;
import com.mongodb.WriteResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Criteria;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Query;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Update;
//Impl postfix of the name on it compared to the core repository interface
public class DomainRepositoryImpl implements DomainRepositoryCustom {
@Autowired
MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Override
public int updateDomain(String domain, boolean displayAds) {
Query query = new Query(Criteria.where("domain").is(domain));
Update update = new Update();
update.set("displayAds", displayAds);
WriteResult result = mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query, update, Domain.class);
if(result!=null)
return result.getN();
else
return 0;
4.3.3 DomainRepository extends the custom interface DomainRepositoryCustom
package com.mkyong.domain;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.Query;
import java.util.List;
public interface DomainRepository extends MongoRepository<Domain, Long>, DomainRepositoryCustom {
//other methods
5. Run
5.1 Spring Boot application.
package com.mkyong;
import com.mkyong.domain.Domain;
import com.mkyong.domain.DomainRepository;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
@Bean
CommandLineRunner init(DomainRepository domainRepository) {
return args -> {
Domain obj = domainRepository.findOne(7L);
System.out.println(obj);
Domain obj2 = domainRepository.findFirstByDomain("mkyong.com");
System.out.println(obj2);
int n = domainRepository.updateDomain("mkyong.com", true);
System.out.println("Number of records updated : " + n);
};
5.2 Gradle build and run it.
$ gradle build $ java -jar build/libs/spring-data-mongodb-example-1.0.jar . ____ _ __ _ _ /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \ ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \ \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) ) ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / / =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/ :: Spring Boot :: (v1.5.1.RELEASE) //blah blah blah
6. FAQs
6.1 How to create a custom MongoTemple?
A : Declares a new MongoTemplate bean to override the default. In below example, it creates a custom MongoTemplate to remove the _class field.
package com.mkyong;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.MongoDbFactory;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.convert.DefaultDbRefResolver;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.convert.DefaultMongoTypeMapper;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.convert.MappingMongoConverter;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.MongoMappingContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
//remove _class
@Bean
public MongoTemplate mongoTemplate(MongoDbFactory mongoDbFactory,
MongoMappingContext context) {
MappingMongoConverter converter =
new MappingMongoConverter(new DefaultDbRefResolver(mongoDbFactory), context);
converter.setTypeMapper(new DefaultMongoTypeMapper(null));
MongoTemplate mongoTemplate = new MongoTemplate(mongoDbFactory, converter);
return mongoTemplate;
References
- Spring Data MongoDB – Reference Documentation
- Working with NoSQL technologies
- Spring Boot Gradle plugin
- Building an Application with Spring Boot
- Gradle – Display project dependency
From:一号门

COMMENTS