JSF 2 + Log4j Integration Example

In this tutorial, we will show you how to integrate the log4j framework with the JSF 2.x web application. JSF is using java.util.logging, you need extra works to redirect the logging from JSF’s java.util.logging to log4j, with a serious penalty of performance, make sure use this trick only during local development or debugging environment.
Review the project environment :
SLF4j 1.7.7
Log4j 1.2.17
JSF 2.2.7
Maven 3
Tomcat 6
Eclipse Kepler 4.3
Steps to integrate JSF and log4j, in short.
Turn on the JSF logging on logging.properties, since this project is running inside the Eclipse environment, the Eclipse’s JRE/lib/logging.properties will be used.
Create a log4j.properties and put it on the class path.
Create a Servlet’s listener, install the slf4j bridge handler to redirect the logging from java.util.logging to log4j.
Note
Refer to this SLF4j Bridging legacy APIs
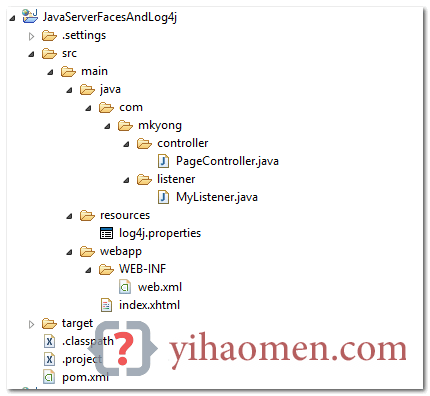
1. Project Directory
Review the final project structure.
2. Project Dependencies
You need slf4j-log4j12 and jul-to-slf4j.
pom.xml
<properties>
<jdk.version>1.7</jdk.version>
<jsf.version>2.2.7</jsf.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.7</slf4j.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- from java.util.logging to log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jul-to-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- it help to get slf4j and log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSF -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.faces</groupId>
<artifactId>jsf-api</artifactId>
<version>${jsf.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.faces</groupId>
<artifactId>jsf-impl</artifactId>
<version>${jsf.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- you need this in web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>4. JSF Logging
Since this project is running inside the Eclipse’s environment, the Eclipse’s JRE will be used. Open the logging.properties, change the level to FINEST, and turn on the logging on javax.faces and com.sun.faces :
${JRE_PATH}/lib/logging.properties
# Default is INFO, change it to FINNEST #java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.level = INFO java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.level = FINEST java.util.logging.ConsoleHandler.formatter = java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter #Add these two lines to enable JSF logging javax.faces.level = FINEST com.sun.faces.level = FINEST
Refer to the java.util.logging levels.
Note
If this project is deployed on Tomcat directly, update this ${Tomcat}\conf\logging.properties
5. Log4j Logging
Create a log4j properties file, and put it into the resources folder, refer to step#1.
log4j.properties
# Root logger option
log4j.rootLogger=WARN, console, file
#enable JSF logging
log4j.logger.javax.faces=DEBUG
log4j.logger.com.sun.faces=DEBUG
# Redirect log messages to console
log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
# Redirect log messages to a log file
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=${catalina.home}/logs/jsfapp.log
log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=5KB
log4j.appender.file.MaxBackupIndex=5
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n6. ServletContextListener
Create a Servlet listener to install the bridge handler, in order to redirect the JSF’s logging from java.util.properties to log4j.
MyListener
package com.mkyong.listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import org.slf4j.bridge.SLF4JBridgeHandler;
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent arg) {
System.out.println("contextInitialized....");
//remove the jsf root logger, avoid duplicated logging
//try comment out this and see the different on the console
SLF4JBridgeHandler.removeHandlersForRootLogger();
SLF4JBridgeHandler.install();
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent arg) {
System.out.println("contextDestroyed....");Include the listener class, and other standard JSF settings.
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5"> <display-name>JavaServerFacesAndLog4j</display-name> <context-param> <param-name>javax.faces.PROJECT_STAGE</param-name> <param-value>Development</param-value> </context-param> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>faces/index.xhtml</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <!-- Install slf4j bridge handler --> <listener> <listener-class> com.mkyong.listener.MyListener </listener-class> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.jsf</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.faces</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.xhtml</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
7. Application Logging
A simple example to show you how to do log4j’s logging.
WelcomeAction.java
package com.mkyong.controller;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
@ManagedBean
@SessionScoped
public class PageController implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(PageController.class);
public String process() {
// logs debug
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("PageController.process()");
// logs exception
logger.error("This is Error message", new Exception("Testing"));
return "success";A simple JSF view resource.
pages/welcome.jsp
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html">
<h:body>
<h1>JSF 2.0 + Log4j</h1>
<h:form>
<h:commandButton action="#{pageController.process}" value="Click Me" />
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>8. Demo
Run the JSF web application, and access the default page, and clicks on the button.
URL : http://localhost:8080/JavaServerFacesAndLog4j/
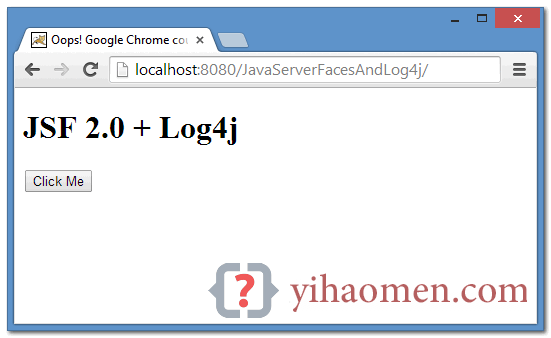
8.1 Both JSF and application logging will be displayed in the console.
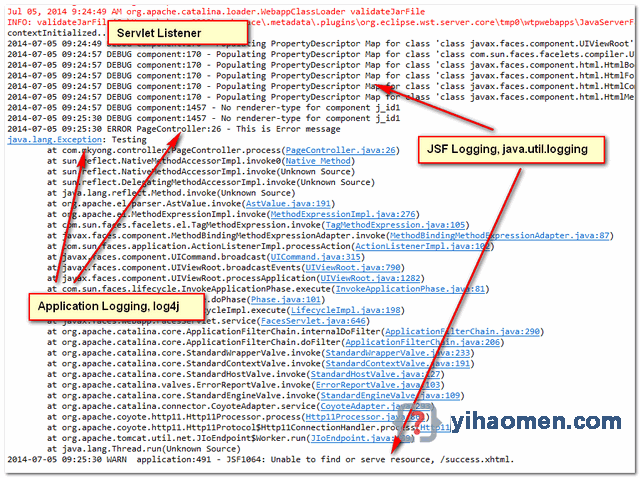
Figure : Eclipse console
8.2 Both JSF and application logging will be logged in ${tomcat}\logs\jsfapp.log.
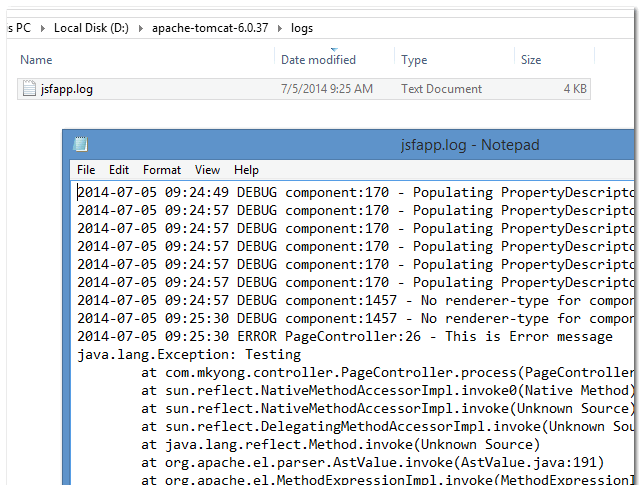
Figure : D:\apache-tomcat-6.0.37\logs\jsfapp.log
References
From:一号门
Previous:Log4j Tutorial

COMMENTS