MongoDB Aggregate and Group example
In this tutorial, we will show you how to use MongoDB aggregate function to group documents (data).
1. Test Data
Data in JSON format, shows the hosting provider for website.
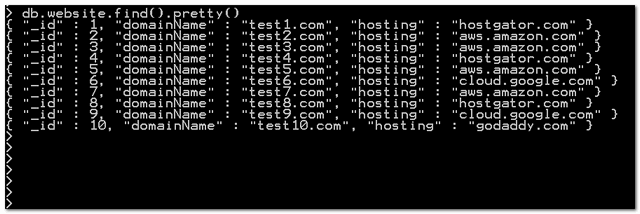
{ "_id" : 1, "domainName" : "test1.com", "hosting" : "hostgator.com" }
{ "_id" : 2, "domainName" : "test2.com", "hosting" : "aws.amazon.com"}
{ "_id" : 3, "domainName" : "test3.com", "hosting" : "aws.amazon.com" }
{ "_id" : 4, "domainName" : "test4.com", "hosting" : "hostgator.com" }
{ "_id" : 5, "domainName" : "test5.com", "hosting" : "aws.amazon.com" }
{ "_id" : 6, "domainName" : "test6.com", "hosting" : "cloud.google.com" }
{ "_id" : 7, "domainName" : "test7.com", "hosting" : "aws.amazon.com" }
{ "_id" : 8, "domainName" : "test8.com", "hosting" : "hostgator.com" }
{ "_id" : 9, "domainName" : "test9.com", "hosting" : "cloud.google.com" }
{ "_id" : 10, "domainName" : "test10.com", "hosting" : "godaddy.com" }
Imports into a “website” collection.
> mongoimport -d testdb -c website --file website.json connected to: 127.0.0.1 Mon Jan 13 14:30:22.662 imported 10 objects
If the collection is existed, add --upsert option to override the data.
> mongoimport -d testdb -c website --file website.json --upsert
2. Grouping Example
Uses db.collection.aggregate and $group to perform the data grouping.
2.1 The following example groups by the “hosting” field, and display the total sum of each hosting.
> db.website.aggregate(
{
$group : {_id : "$hosting", total : { $sum : 1 }}
);
Output
"result" : [
"_id" : "godaddy.com",
"total" : 1
},
"_id" : "cloud.google.com",
"total" : 2
},
"_id" : "aws.amazon.com",
"total" : 4
},
"_id" : "hostgator.com",
"total" : 3
],
"ok" : 1
The equivalent SQL.
SELECT hosting, SUM(hosting) AS total
FROM website
GROUP BY hosting
2.2 Add sorting with $sort.
> db.website.aggregate(
{
$group : {_id : "$hosting", total : { $sum : 1 }}
},
$sort : {total : -1}
);
Output – Display “total” in descending order. For ascending order, uses $sort : {total : 1}.
"result" : [
"_id" : "aws.amazon.com",
"total" : 4
},
"_id" : "hostgator.com",
"total" : 3
},
"_id" : "cloud.google.com",
"total" : 2
},
"_id" : "godaddy.com",
"total" : 1
],
"ok" : 1
2.3 Add $match condition, groups by “hosting” for “aws.amazon.com” only.
> db.website.aggregate(
{
$match : {hosting : "aws.amazon.com"}
},
{
$group : { _id : "$hosting", total : { $sum : 1 } }
);
Output
"result" : [
"_id" : "aws.amazon.com",
"total" : 4
],
"ok" : 1
Refer to this official MongoDB Aggregation guide for more advance aggregation and group examples.
3. Exports Grouping Result to CSV or JSON
Often times, we need to export the grouping results in csv or JSON format. To solve it, inserts the group results in a new collection, and exports the new collection via mongoexport.
3.1 Set the group results in a variable. In this case, the variable name is “groupdata”.
> var groupdata = db.website.aggregate(
{
$group : {_id : "$hosting", total : { $sum : 1 }}
},
$sort : {total : -1}
);
3.2Inserts groupdata.toArray() into a new collection.
> db.websitegroup.insert(groupdata.toArray());
> db.websitegroup.find().pretty()
{ "_id" : "aws.amazon.com", "total" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "hostgator.com", "total" : 3 }
{ "_id" : "cloud.google.com", "total" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "godaddy.com", "total" : 1 }
>
3.3 Exports the collection “websitegroup” to a csv file.
c:\> mongoexport -d testdb -c websitegroup -f _id,total -o group.csv --csv connected to: 127.0.0.1 exported 4 records
_id,total "aws.amazon.com",4.0 "cloud.google.com",2.0 "godaddy.com",1.0 "hostgator.com",3.0
3.4 Exports the collection “websitegroup” to a JSON file.
c:\> mongoexport -d testdb -c websitegroup -o group.json connected to: 127.0.0.1 exported 4 records
{ "_id" : "aws.amazon.com", "total" : 4 }
{ "_id" : "cloud.google.com", "total" : 2 }
{ "_id" : "godaddy.com", "total" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "hostgator.com", "total" : 3 }
4. Large Sort Operation
In MongoDB, the in-memory sorting have a limit of 100M, to perform a large sort, you need enable allowDiskUse option to write data to a temporary file for sorting.
To avoid the sort exceeded memory limit error, enable the allowDiskUse option.
db.website.aggregate(
{$group : {_id : "$hosting", total : { $sum : 1 }}},
{$sort : {total : -1}}
],
{allowDiskUse: true}
);
References
- MongoDB Aggregation
- MongoDB db.collection.aggregate()
- Aggregation Pipeline Limits
- MongoDB Hello World Example
From:一号门

COMMENTS