利用easyexcel生成excel文件-复杂表头/多表头/自定义表头设计
By:Roy.LiuLast updated:2020-12-02
在上一篇文章( http://www.yihaomen.com/article/1850.html ) 测试了easyexcel生成简单的EXCEL文件,继续测试利用easyexcel生成复杂表头,或者自定义表头的设计。
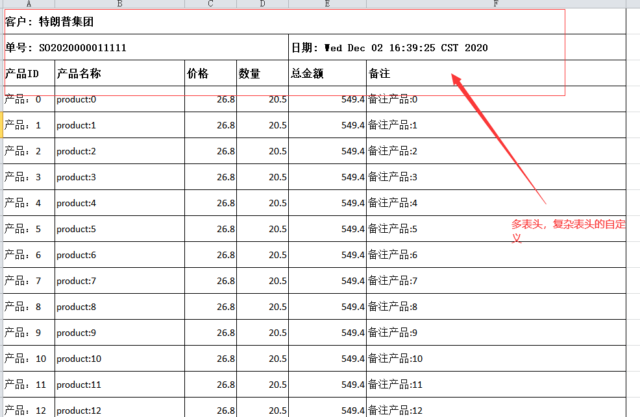
既然是多表头,复杂的自定义表头设计,原来利用注解来实现单元格的宽度,样式等都不能用了,这个时候需要自定义指定参数,测试还是用上一篇文章提到的订单来做,最终实现的效果如下:
先上代码,然后在稍稍解释一下:
package com.yihaomen.myexcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.CellData;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Head;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.handler.WriteHandler;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.holder.WriteSheetHolder;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.holder.WriteTableHolder;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.style.WriteCellStyle;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.metadata.style.WriteFont;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.HorizontalCellStyleStrategy;
import com.alibaba.excel.write.style.column.AbstractColumnWidthStyleStrategy;
import com.yihaomen.myexcel.domain.Detail;
import com.yihaomen.myexcel.domain.Master;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import sun.security.x509.CertAttrSet;
import java.io.File;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class WriteExcel_1 {
private Master master;
private List<Detail> details = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 初始化测试数据
*/
@Before
public void initData() {
master = new Master();
master.setCustomer("特朗普集团");
master.setSheetNo("SO2020000011111");
master.setCreatedDate(new Date());
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
Detail d = new Detail();
d.setProductId("product:" + i);
d.setProductName("产品:" + i);
d.setPrice(new BigDecimal("26.80"));
d.setNumber(new BigDecimal("20.5"));
d.setAmount(d.getPrice().multiply(d.getNumber()));
d.setMemo("备注产品:" + i);
details.add(d);
}
}
/**
* 仅仅输出明细数据到excel文件
*/
@Test
public void writeSimpleExcelForDetail() {
String path = this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
System.out.println(path);
String fileName = path + File.separator + "writeSimpleExcel.xlsx";
// 这里 需要指定写用哪个class去写,指定模板名称及数据
EasyExcel.write(fileName, Detail.class).sheet("sheet名称").doWrite(details);
}
/**
* 仅仅输出明细数据到excel文件, 排除部分字段
*/
@Test
public void writeSimpleExcelExculdeColumns() {
String path = this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
List<String> excludeColumns = new ArrayList<>();
excludeColumns.add("memo");
String fileName = path + File.separator + "writeSimpleExcel.xlsx";
// 这里 需要指定写用哪个class去写,指定模板名称及数据
EasyExcel.write(fileName, Detail.class).excludeColumnFiledNames(excludeColumns).sheet("sheet名称").doWrite(details);
}
/**
* 仅仅输出明细数据到excel文件, 增加自定义的头部
*/
@Test
public void writeSimpleExcelWithHeader() {
String path = this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
String fileName = path + File.separator + "writeSimpleExcel.xlsx";
// 准备 HEADER
List<List<String>> list = getHeader();
// 这里 需要指定写用哪个class去写,指定模板名称及数据
EasyExcel.write(fileName).head(list).registerWriteHandler(new CustomizeColumnWidth())
.registerWriteHandler(getStyleStrategy()).sheet("sheet名称").doWrite(details);
}
private List<List<String>> getHeader() {
/**
* 打算展示成如下样子
* |客户:xxx 公司 (这一行需要合并单元格)
* |单号: SO22222222222222| 日期: 2020-01-01 (分别需要合并单元格)
* |产品ID|产品名称|价格|数量|总金额|备注|
*/
String customer = "客户: " + master.getCustomer();
String sheetNo = "单号: " + master.getSheetNo();
String dateStr = "日期: " + master.getCreatedDate();
List<List<String>> list = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> head0 = new ArrayList<String>();
head0.add(customer);
head0.add(sheetNo);
head0.add("产品ID");
List<String> head1 = new ArrayList<String>();
head1.add(customer);
head1.add(sheetNo);
head1.add("产品名称");
List<String> head2 = new ArrayList<String>();
head2.add(customer);
head2.add(sheetNo);
head2.add("价格");
List<String> head3 = new ArrayList<String>();
head3.add(customer);
head3.add(sheetNo);
head3.add("数量");
List<String> head4 = new ArrayList<String>();
head4.add(customer);
head4.add(dateStr);
head4.add("总金额");
List<String> head5 = new ArrayList<String>();
head5.add(customer);
head5.add(dateStr);
head5.add("备注");
list.add(head0);
list.add(head1);
list.add(head2);
list.add(head3);
list.add(head4);
list.add(head5);
return list;
}
private HorizontalCellStyleStrategy getStyleStrategy() {
// 头的策略
WriteCellStyle headWriteCellStyle = new WriteCellStyle();
// 设置对齐
headWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.LEFT);
// 背景色, 设置为白色,也是默认颜色
headWriteCellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.WHITE.getIndex());
// 字体
WriteFont headWriteFont = new WriteFont();
headWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
headWriteCellStyle.setWriteFont(headWriteFont);
// 内容的策略
WriteCellStyle contentWriteCellStyle = new WriteCellStyle();
// 这里需要指定 FillPatternType 为FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND 不然无法显示背景颜色.头默认了 FillPatternType所以可以不指定
// contentWriteCellStyle.setFillPatternType(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
// contentWriteCellStyle.setFillPatternType(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
// 背景绿色
//contentWriteCellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.getIndex());
// 字体策略
WriteFont contentWriteFont = new WriteFont();
contentWriteFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
contentWriteCellStyle.setWriteFont(contentWriteFont);
//设置 自动换行
contentWriteCellStyle.setWrapped(true);
//设置 垂直居中
contentWriteCellStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
//设置 水平居中
// contentWriteCellStyle.setHorizontalAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
//设置边框样式
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentWriteCellStyle.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
// 这个策略是 头是头的样式 内容是内容的样式 其他的策略可以自己实现
HorizontalCellStyleStrategy horizontalCellStyleStrategy = new HorizontalCellStyleStrategy(headWriteCellStyle, contentWriteCellStyle);
return horizontalCellStyleStrategy;
}
/**
* 自定义头部的 列的宽度设置 策略. .
*/
class CustomizeColumnWidth extends AbstractColumnWidthStyleStrategy {
@Override
protected void setColumnWidth(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, List<CellData> list, Cell cell, Head head, Integer integer, Boolean isHead) {
// 测试为 COLUMN 宽度定制.
if (isHead && cell.getRowIndex() == 2) {
int columnWidth = cell.getStringCellValue().getBytes().length;
int cellIndex = cell.getColumnIndex();
switch (cellIndex) {
case 0:
case 2:
case 3:
columnWidth = 10;
break;
case 1:
columnWidth = 25;
break;
case 4:
columnWidth = 15;
break;
case 5:
columnWidth = 50;
break;
default:
break;
}
if (columnWidth > 255) {
columnWidth = 255;
}
writeSheetHolder.getSheet().setColumnWidth(cellIndex, columnWidth * 256);
}
}
@Override
public void beforeCellCreate(WriteSheetHolder writeSheetHolder, WriteTableHolder writeTableHolder, Row row, Head head, Integer columnIndex, Integer relativeRowIndex, Boolean isHead) {
// 设置行高测试
int rowIndex = row.getRowNum();
System.out.println("当前行: " + rowIndex);
short height = 600;
row.setHeight(height);
}
}
}测试方式是 writeSimpleExcelWithHeader, 其中通过 getHeader() 方法去得到自定义表头, 注意自定义表头合并部分的写法, 另外,自定义表头样式是通过 getStyleStrategy()方法得到的,头部样式与内容样式是分开设置的。另外对于行高,列框是通过实现了easyexcel 里面提供的方法实现的, 也就是自定义类 CustomizeColumnWidth .
最终生成excel的部分代码,只有少许差别:
EasyExcel.write(fileName).head(list).registerWriteHandler(new CustomizeColumnWidth())
.registerWriteHandler(getStyleStrategy()).sheet("sheet名称").doWrite(details);其实里面还是用的POI的方法,通过实现 WriteHandler可以实现很多自己想要的功能。
From:一号门

COMMENTS