Spring Security Basic Authentication Configuration Example
The following tutorial is about Spring Security Basic Authentication Configuration. We demonstrate this by configuring Spring Security using both Java and XML Configuration. We create a custom authentication entry point which we can use and customize to give the user a custom login error message. We finish with showing how to write some integration tests using Spring MockMvc and JUnit.
Maven Dependencies
We use Apache Maven to manage our project dependencies. Make sure the following dependencies reside on the class-path.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.memorynotfound.spring.security</groupId>
<artifactId>basic-authentication</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<url>http://memorynotfound.com</url>
<name>Spring Security - ${project.artifactId}</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.8.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- testing -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Spring Security Basic Authentication Configuration
Basic authentication is mainly used in web applications. Basic authentication is often used with stateless clients which pass their credentials on each request. It’s quite common to use it in combination with form-based authentication where an application is used through both a browser-based user interface and as a web-service. However, basic authentication transmits the pasword as plain text so it should only really be used over an encrypted transport layer such as HTTPS.Spring Java Configuration
The following Spring Java Configuration configures Spring Security to use HTTP Basic Authentication.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.config;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
public static final String REALM_NAME = "memorynotfound.com";
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf()
.disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.realmName(REALM_NAME)
.authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint());
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER")
.and()
.withUser("manager").password("password").roles("MANAGER");
}
}Spring Security Xml Configuration
The following is the equivalent Spring XML Configuration.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beans:bean id="basicAuthEntryPoint" class="com.memorynotfound.spring.security.config.CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint"/>
<http realm="memorynotfound.com">
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="isAuthenticated()"/>
<http-basic entry-point-ref="basicAuthEntryPoint"/>
<csrf disabled="true"/>
</http>
<authentication-manager>
<authentication-provider>
<user-service>
<user name="user" password="password" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
<user name="manager" password="password" authorities="ROLE_MANAGER" />
</user-service>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
</beans:beans>Custom Authentication Entry Point
We can extend the BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint to intercept the error message before it is sent to the client. This way we can control what we sent as a response.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.config;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint extends BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
response.setHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=" + getRealmName());
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE);
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("HTTP Status 401 : " + authException.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
setRealmName(SecurityConfig.REALM_NAME);
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}Spring Boot
We create a simple rest controller which maps to the root of the application.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.web;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String greeting() {
return "Hello, World!";
}
}We use Spring Boot to start our application.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
@SpringBootApplication
// # enable if you want to use spring xml configuration
// @ImportResource("classpath:spring-security-config.xml")
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Run.class, args);
}
}
Demo
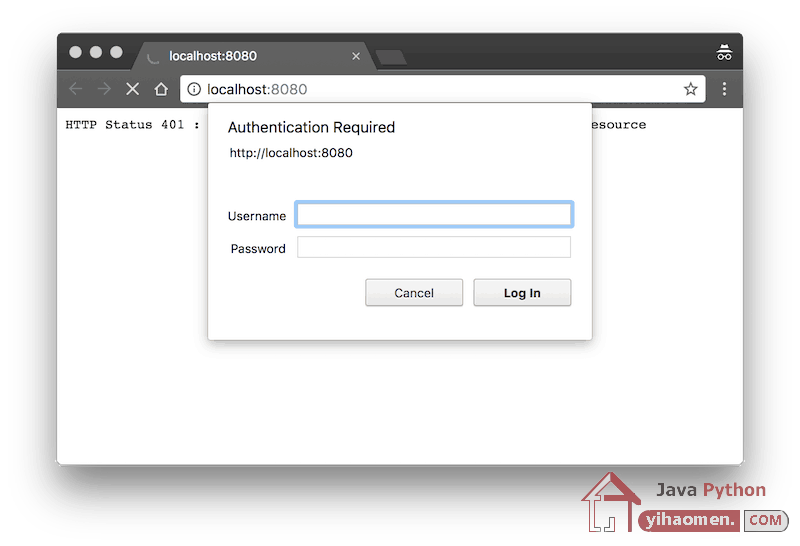
Access http://localhost:8080 and receive the basic authentication login popup.
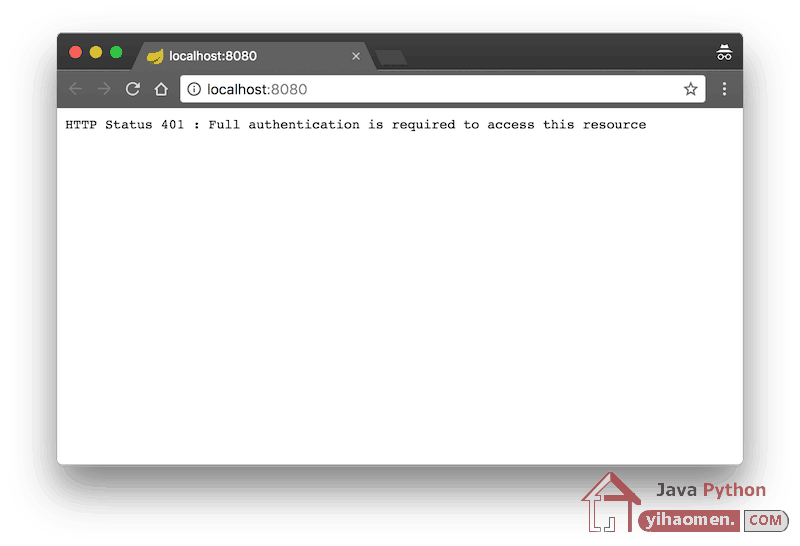
When we cancel the basic authentication login popup.
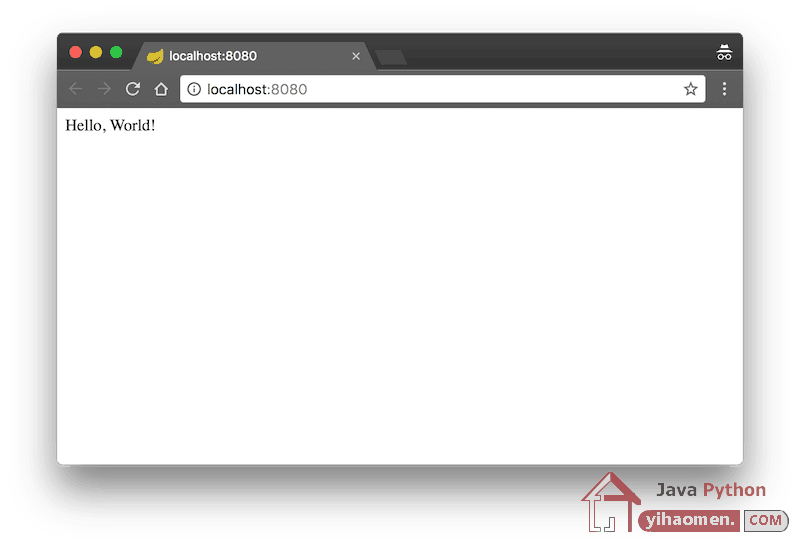
After successful login, redirects to http://localhost:8080.
Spring Security Basic Authentication Integration Test
We can write some Integration Tests using JUnit and spring-test with MockMvc.
package com.memorynotfound.spring.security.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MvcResult;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
import static org.springframework.security.test.web.servlet.request.SecurityMockMvcRequestBuilders.formLogin;
import static org.springframework.security.test.web.servlet.request.SecurityMockMvcRequestPostProcessors.httpBasic;
import static org.springframework.security.test.web.servlet.response.SecurityMockMvcResultMatchers.authenticated;
import static org.springframework.security.test.web.servlet.response.SecurityMockMvcResultMatchers.unauthenticated;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class BasicAuthenticationIntegrationTests {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void accessProtected() throws Exception {
this.mockMvc.perform(get("/"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
@Test
public void loginUser() throws Exception {
this.mockMvc.perform(get("/").with(httpBasic("user", "password")))
.andExpect(authenticated());
}
@Test
public void loginInvalidUser() throws Exception {
MvcResult result = this.mockMvc.perform(formLogin().user("invalid").password("invalid"))
.andExpect(unauthenticated())
.andExpect(status().is4xxClientError())
.andReturn();
assertTrue(result.getResponse().getContentAsString().contains("HTTP Status 401"));
}
}Spring Security JUnit Integration Test Results
Download
下一篇: Adding Static Resources (css, JavaScript, Images) to Thymeleaf